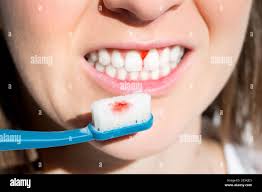
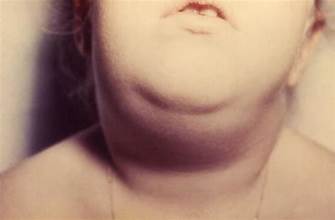
Scurvy Disease caused by a severe deficiency of vitamin C, which results from the inadequate amount of vitamin C in the food that is used daily, such as foods and vegetables. This disease is found around the world where people are malnourished.
What is vitamin C?
Vitamin C, commonly known as ascorbic acid, is a very important nutrient for the human body. Vitamin C is important for the better development, growth, and healing of skin, bones, and connective tissues. Moreover, over vitamin C is needed for blood vessels to function properly. It helps the human body to absorb iron, which is needed to make red blood cells. Vitamin C is also important to heal burns and wounds. It is an antioxidant, which protects human body cells against damage from free radicals.
Who is most susceptible to scurvy?
Scurvy most commonly affects babies, children, and older adults who don’t get an adequate amount of vitamin C in their diet. How widespread is scurvy in modern times? There are many centuries around the world where people are affected by vitamin C deficiency. The rate of vitamin C deficiency is 7.1% of people having vitamin C deficiency in the U.S. About 73.9% of people experienced vitamin C deficiency in North India.
Symptoms of scurvy:
Scurvy is a common disease, but it is not severe. Its symptoms may start to develop after a few months of not getting an adequate amount of vitamin C in your diet. Their symptoms may include weakness, feeling tired, fatigue, irritability, and joint pain. If this disease is left untreated, its severe symptoms may start developing in the person’s body. These severe symptoms may include Anemia (a disease that is caused by a lower number of RBCs in the body). Swallow, bleeding gums that may become purple and spongy. Very weak, loosened teeth that may fall out. Skin hemorrhages (bleeding under your skin). Scurvy rashes that show up as red or blue spots on your skin. Very rough and scaly skin. Legs become swollen. Delay in healing of the wound, even at times, opening of previously healed wounds. Very dry and brittle hair. In babies and children, these symptoms may be found. Babies become so irritable They feel pain when they are moving. They are losing their appetite. They are unable to gain weight (underweight). Children become anemic.
Causes of scurvy:
A major cause of this disease is the severe lack of vitamins in your diet for more than 3 months. This deficiency includes not eating enough fresh fruits and vegetables, which contain vitamin C. Vitamin C is needed for every person to stay safe from this disease. In certain cases, you need more vitamin C, such as during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or in case of high fevers. Vitamin C is needed more when you have an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism), chronic diarrhea, recent surgery, burns, or tobacco usage. In these cases, person’s body needs more vitamin C.
Diagnosis of scurvy:
For the diagnosis of scurvy, you need to visit a healthcare professional. Based on the symptoms, the advisor can prefer some test that clinically proves that a person is having scurvy disease. In addition, they may perform a test called a dermoscopy with this procedure. In this process, a sample of hair or damaged skin is taken and examined using a microscope.
Treatment for scurvy:
To avoid complications caused by scurvy, its treatment is very important. This is a very treatable disease; it can be treated easily by using more vitamin C-containing products in the diet. At least you should try to maintain a nutritious diet, including vitamin C in it, one or two times daily. This can be done by using fresh fruit and vegetables containing vitamin c in them to avoid further complications of scurvy. A healthcare provider may also recommend a vitamin C supplement until a person feels better. Children having scurvy can take a supplement of up to 300 milligrams (mg) daily. Adults can take supplements between 500 mg and 1000 mg.
How to prevent scurvy?
To prevent scurvy, you have to take an adequate amount of vitamin C in your daily diet. The best sources of vitamin which can be easily available and have plenty of vitamin C in them, which can reduce the risk of scurvy are citrus fruits, tomatoes, potatoes, broccoli, strawberries, and sweet peppers.
Conclusion:
Scurvy, though an ancient disease, still exists today in areas where malnutrition and poor dietary habits are common. It arises from a prolonged deficiency of vitamin C, a vital nutrient for healthy skin, bones, blood vessels, and overall body repair. While its symptoms can progress from mild fatigue and irritability to severe complications such as bleeding gums, anemia, and delayed wound healing, the disease is both preventable and highly treatable. Maintaining a diet rich in vitamin C—through fresh fruits, vegetables, or supplements—remains the simplest and most effective way to prevent scurvy. Early recognition of its symptoms and timely treatment not only reverse the disease quickly but also protect individuals from its serious consequences. Ultimately, awareness about balanced nutrition is the key to eradicating scurvy in modern times.