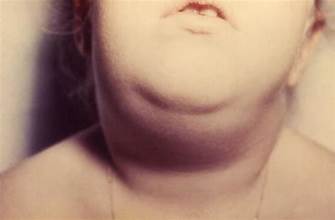
What Is Mumps?
Mumps is a contagious viral disease caused by the mumps virus, which belongs to the paramyxovirus family. It mainly affects the parotid salivary glands, located in front of and below each ear, leading to noticeable swelling and pain. These glands are responsible for producing saliva, which helps with digestion and oral health.
The virus spreads easily from person to person through coughing, sneezing, saliva, close contact, and by touching contaminated objects such as shared utensils, tissues, or unwashed hands.
How Mumps Affects the Body?
After entering the body, the virus travels through the bloodstream and may infect several organs, including:
- Salivary glands: Causes swelling, tenderness, and pain around the jaw and cheeks.
- Testes: In males, mumps can lead to testicular swelling and discomfort. In rare cases, it may cause long-term shrinkage, but infertility is uncommon.
- Ovaries: In females, ovarian involvement may cause lower abdominal pain but usually does not affect fertility.
- Pancreas: Infection can result in inflammation, leading to abdominal pain and digestive discomfort.
- Brain: In rare cases, the virus can cause meningitis or encephalitis, which may lead to serious complications such as hearing loss, facial muscle weakness, seizures, or fluid buildup in the brain.
Although severe complications are uncommon, mumps can cause long-term health problems in some individuals. Vaccination remains the most effective way to prevent mumps and protect against its complications.
Who Is Most at Risk for Mumps?
Mumps mainly occurs in children aged 2 to 12 years who have not received the mumps vaccine. However, teenagers and adults can also become infected, even if they were vaccinated earlier in life. This happens because vaccine protection may decrease gradually over time.
Despite this, vaccination remains the most reliable and effective method for preventing mumps and reducing the risk of outbreaks and complications. Staying up to date with recommended vaccine doses offers the strongest protection against infection.
Mumps Symptoms and Causes:
What Are the Symptoms of Mumps?
Mumps often begins with mild or unnoticed symptoms. Some people may not realize they are infected at all. After exposure, symptoms usually appear within 7 to 25 days, which is known as the incubation period.
Early symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Body and muscle pain
- Tiredness
- Poor appetite
After a few days, many patients develop swelling of the parotid glands, which are salivary glands located near the ears and jaw. This swelling, called parotitis, may affect one or both sides of the face. It causes puffed cheeks and jaw enlargement, giving the face a rounded appearance. Parotid gland swelling is seen in most mumps cases.
However, not all cases of parotid swelling are caused by mumps, as other infections can produce similar symptoms.In rare situations, mumps can spread to other organs such as:
- Brain
- Pancreas
- Testicles
- Ovaries
These complications are more common in teenagers and adults. Seek medical attention immediately if any of the following symptoms occur:
- Very high fever
- Stiff neck
- Severe headache
- Confusion or unusual behavior
- Abdominal pain
- Repeated vomiting
- Seizures
What Causes Mumps?
Mumps is caused by the mumps virus, a member of the paramyxovirus family. The virus spreads easily through contact with infected saliva or respiratory droplets from the nose, mouth, or throat.
The infection can spread when an infected person:
- Coughs, sneezes, or talks
- Shares cups, utensils, or toys
- Participates in close-contact activities such as sports, dancing, or kissing
Who Is at Higher Risk?
Certain groups are more likely to contract mumps, including:
- People with weakened immune systems
- International travelers
- Individuals who are not vaccinated
- People living in crowded settings such as hostels, dormitories, or college campuses
Vaccination remains the most effective way to prevent mumps and its complications.
How Is Mumps Diagnosed?
Mumps is usually diagnosed by evaluating a person’s symptoms, medical history, and any recent contact with someone who has had the infection. Swelling of the salivary glands, along with fever and fatigue, often gives doctors an early clue.
To confirm the diagnosis, healthcare providers may perform several tests, including:
- Oral swab: A sample taken from the inside of the mouth to detect the mumps virus.
- Urine test: Used to identify viral genetic material.
- Blood test: Checks for antibodies that the body produces in response to the mumps virus.
In some cases, advanced laboratory methods such as PCR testing are used to accurately identify the virus from collected samples.
Doctors may also rule out other conditions that cause similar symptoms, such as bacterial infections, influenza, or other viral illnesses affecting the salivary glands.
Early and accurate diagnosis helps limit the spread of infection and ensures proper monitoring for possible complications.
Management and Care for Mumps:
There is no direct cure for mumps. The infection usually resolves on its own within one to two weeks, and treatment mainly focuses on easing discomfort and supporting recovery.
To help relieve symptoms, you can:
- Drink plenty of water and other fluids to stay hydrated
- Rinse the mouth with warm salt water to reduce throat discomfort
- Choose soft, easy-to-swallow foods such as soups, yogurt, or mashed foods
- Avoid sour or acidic foods that stimulate saliva and increase pain
- Suck on ice pops to soothe a sore throat
- Apply warm or cold compresses to swollen glands for comfort
- Use non-aspirin pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce fever and body aches
Rest is also important, as it helps the body fight the infection more effectively. If symptoms worsen or complications appear, a healthcare provider should be contacted for further evaluation.
prevention of Mumps:
Mumps can be effectively prevented through vaccination, most commonly with the MMR vaccine (measles, mumps, and rubella). This vaccine provides strong, long-lasting protection against mumps and is part of the routine childhood immunization schedule. However, because it contains a live weakened virus, it is usually not recommended for pregnant individuals or for people with severely weakened immune systems.
Since people with mumps can spread the virus one to two days before symptoms appear, household members are often already exposed by the time the illness is recognized. For this reason, strict isolation at home is usually not required once symptoms begin.
Children diagnosed with mumps are typically kept out of school or childcare settings for five days after the swelling of the salivary glands starts to reduce the risk of spreading the infection. Public health authorities may also monitor and manage outbreaks in schools, colleges, and communities.
Maintaining good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and staying up to date with vaccinations are the best ways to protect against mumps and prevent outbreaks.
How Long Does Mumps Last?
Mumps symptoms usually continue for about 7 to 10 days, although full recovery may take up to two weeks in some people. Swelling of the salivary glands often improves within a few days, while fatigue and weakness may last slightly longer.
Most individuals begin to feel better once the fever goes down and the gland swelling starts to subside. Children typically recover faster than adults, who may experience more prolonged discomfort.
After recovering from mumps, the body develops long-term immunity, meaning it is very unlikely for a person to get infected with the mumps virus again. However, maintaining vaccination is still important to protect against other preventable diseases and to help control outbreaks in the community. If symptoms persist beyond two weeks or become more severe, medical advice should be sought.